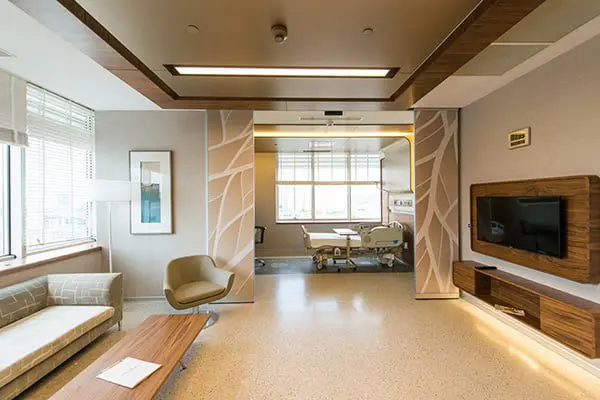
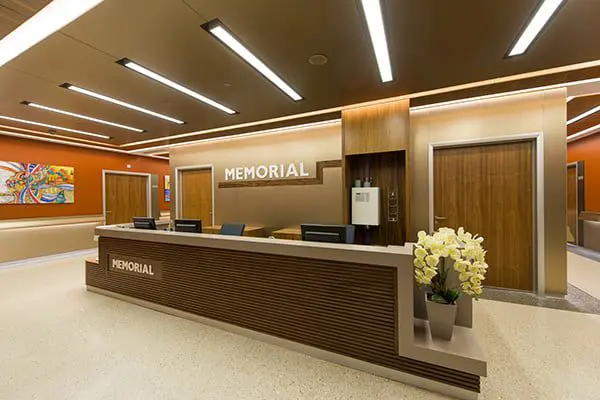
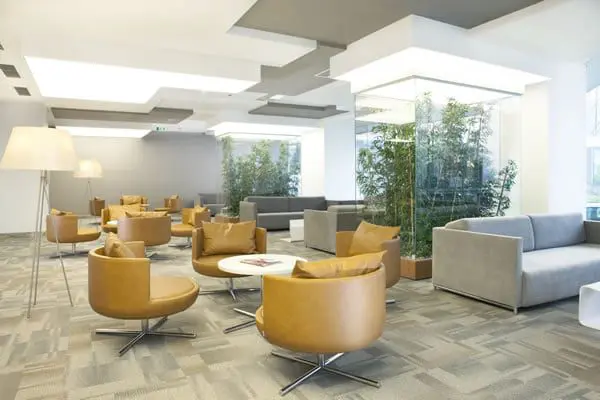
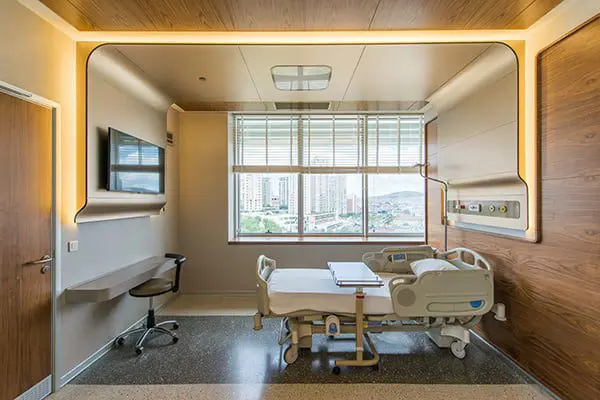
Memorial Ataşehir Hospital is a multidisciplinary hospital in Istanbul. It is part of the largest medical network Memorial. It is equipped with high-tech equipment, the most advanced cancer treatment systems: the new generation Elekta Versa HD SIGNATURE irradiation, robotic surgery, X-ray imaging systems, one of the radiological imaging systems 3 Tesla MR technology, angiographic units for vascular examination, and the clinic also specializes in neurosurgery, cardiac surgery, reproductive medicine and IVF centers, hematology, breast health are popular. Memorial Ataşehir Hospital provides assistance in various areas to patients from all over the world.
Memorial Ataşehir Istanbul
About the clinic

Why us?
Memorial Ataşehir Hospital in Turkey, one of the leading hospitals of the Memorial network. The infrastructure of the hospital is:
- 144 hospital beds (25 of them in the intensive care unit)
- 5 surgical rooms
Areas of Expertise
Due to the high success rates after the procedures (up to 65%), the center is popular among most foreign patients. The following procedures are available:
- classical IVF
- ICSI – the result is at the level of 95%. Doctors perform this procedure mainly in case of male infertility, if the man’s sperm are not very mobile. During ICSI, the reproductive specialist selects the most active sperm and injects it into the egg with a special thin needle.
- IMSI – fertilization by micro-injection. The procedure is similar to ICSI, the only difference is that the doctor uses a more powerful microscope.
- cryopreservation of sperm, eggs and embryos
In addition, preimplantation genetic diagnostics is available for future parents at the hospital. Thanks to screening, parents can be sure that the child does not have hereditary diseases and developmental disorders. The procedure is carried out in each case, but it is especially relevant for people with genetic pathologies, which can affect the bearing of a child. Diagnostics are also recommended for already born children with deviations.
Memorial Ataşehir Hospital Heart Center provides services in the fields of examination, diagnosis, treatment, rehabilitation and coronary intensive care for heart diseases with world-class equipment and infrastructure. Diagnosis and treatment opportunities are provided to all patients with cardiovascular diseases, from newborns (in the fetal cardiology department, where heart defects are diagnosed during pregnancy) to the elderly.
Cardiology Tests at the Memorial Hospital Heart Center
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a recording of the electrical activity of the heart to study the functioning of the heart muscle and neurotransmitter system.
Treadmill Exercise Test – A stress test used to evaluate for cardiovascular disease, to determine the effectiveness of treatment for known cardiovascular disease, to determine if the heartbeat is irregular with effort, to determine if there is an arrhythmia, and to evaluate a patient’s ability to exert effort in various heart conditions. During the exercise test, the patient walks on a treadmill.
Stress echocardiography – used to evaluate for blockage or narrowing of the blood vessels that feed the heart (coronary arteries), to determine the need for treatment other than medication in patients who have had a heart attack (myocardial infarction), and to assess the severity of disease in patients with valvular heart disease. It is safe, easy to use, and provides very important information.
Holter (Holter ECG) – a device that is attached to a belt, 3-4 cables are attached to the chest with electrodes. While the person goes about their daily life, the device measures cardiac electrolytes at scheduled times. After the time has elapsed, the device is removed and the records are analyzed on a computer. This device can detect any rhythm disturbances originating from the heart, such as palpitations, chest pain, and fainting that are not visible on examination but last for a short time during the day.
Event Recorder – devices similar to the Holter ECG and used specifically to detect rhythm disturbances that do not recur frequently. The device can remain with the patient for 14 days. It has the function of recording only when the patient has complaints (the recording time can be customized as desired).
Blood Pressure Holter – measuring the blood pressure of patients at frequent intervals during the day and recording the blood pressure and pulse.
Tilt Table Test – a test used to diagnose syncope caused by a sudden drop in blood pressure and/or heart rate after standing still for a long time or after sitting for a long time. It is used in the differential diagnosis of syncope. The test is performed in a clinic on a tilt table. The patient is placed on the table, then the table is brought to an upright position. An excessive drop in blood pressure and/or a low heart rate indicate an abnormal response.
Interventional interventions
Treatment of aortic valve stenosis (Tavi method)
With age, calcification can be seen in the aortic valve and the valve does not open and close well. Narrowing of the aortic valve due to old age is more common in men. In the TAVI method, which can be considered a revolution in cardiology, a new valve is placed inside the aortic valve using a non-surgical catheter. In this method, the valve is replaced without opening the chest. TAVI, which is the process of widening the narrowed valve by reaching the heart through a vein through a catheter without stopping the heart and opening the chest, and placing a new valve in this widened area, is a method used in patients for whom open surgery is not possible.
Temporary pacemakers
The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia by placing thin wires (electrodes) through large veins that lead to the heart in the neck, chest, or groin and connecting it to a generator outside the body. This procedure can be done at the patient’s bedside or under an X-ray machine. The procedure usually takes 20 to 30 minutes. Once the temporary battery is no longer needed, the wire placed inside the heart is removed.
Catheter ablation
Catheter ablation is the treatment of rhythm disturbances using radio waves. This method is used for rhythm disturbances that do not respond to drug treatment or in cases where patients do not want to take medications for life. The success rate in treating rhythm disturbances in the form of rapid heartbeat with catheter ablation ranges from 70-100%, depending on the type of heartbeat being treated and the location of the short circuit.
Ischemic angiography
Coronary angiography is a technique used to detect diseases of the arteries that feed the heart. This is caused by cardiovascular disease. Coronary angiography also determines which area of the arteries that feed the heart are narrowed or blocked. It identifies stenosis or occlusion of the heart vessels and ensures that treatment is directed as needed. The groin or arm arteries are used as the site of intervention for coronary angiography.
Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTKA) – Stent
Techniques used to treat narrowing or complete occlusion of the vessels feeding the heart, detected after coronary angiography. Like PTCA and/or stent coronary angiography, it is performed in the angiography lab using local anesthesia at the entry site without making the patient drowsy. Treatment time varies. Once the procedure is complete, the patient is transported to the appropriate service as advised by the physician. Coronary balloon angioplasty is performed using specially designed materials.
Myocardial perfusion scintigraphy
This test looks at the blood supply (or nutrition) to the heart muscle at rest and under stress. It looks at whether there is stenosis in the vessels that feed the heart, and if so, whether the stenosis is causing problems with the blood supply to the heart. It is more sensitive than the stress test. First, the patient is injected with radioactive material intravenously and pictures are taken with a device called a gamma camera at rest, then a stress test is done by walking on a tape or with a drug, and the radioactive material is injected again. Again, the picture is taken with a gamma camera. The radioactive material rises to the heart and reaches the heart muscle. In areas where there is occlusion of the vessels, the material is retained less. A gamma camera is the name of the device that allows us to take the pictures. It rotates around the heart at regular intervals and transmits the radioactive signals from the heart to a computer.
Thoracic surgery is a medical subspecialty that deals with surgery for congenital, oncologic, inflammatory, and related conditions that make up the chest cavity (excluding the heart). The organs of interest include the lungs, the mediastinum (the area between the two lungs and inside the heart), the diaphragm, the bones and muscles that make up the chest cavity itself, and the trachea and esophagus. Thoracic surgery departments provide world-class care through experienced staff, advanced technology, and multidisciplinary approaches.
Diagnostic Methods
BRONCHOSCOPY is a procedure performed by entering the trachea. It is used to remove foreign bodies in the bronchi, take biopsies from lesions in the bronchi, or clean out the bronchi.
MEDIASTHENOSCOPY is a procedure performed by inserting a camera into the mediastinum. It is used to sample lesions in the mediastinum, especially from the lymph nodes.
MEDIASTINOTOMY is a surgical procedure performed on the mediastinum to sample lesions in an area that cannot be reached by mediastinoscopy.
ESOPHAGOSCOPY is a procedure performed by entering the esophagus, used to remove foreign bodies from the esophagus and to sample lesions in the esophagus.
Treatment Methods
Thoracic surgery is performed using open and closed methods of treatment. The type of surgical intervention is determined by the patient’s condition, anatomical structure and the condition of the lesion. However, open and closed surgical methods have their own advantages and disadvantages.
Open method: In the open method of surgery, the entry point is selected from the patient’s chest depending on the condition of the lesion. Two or three sutures are used to bring the ribs together after an open operation, which is performed by entering the chest cavity between two ribs. The size of the incision that needs to be made may vary depending on the lesion. This type of surgery is especially preferable when the lesion is large, the disease has reached an advanced stage and there is adhesion to the surrounding tissues.
Closed method: It is used with two different techniques: VATS and Robotic (Da Vinci). VATS (video-assisted thoracic surgery – video-assisted thoracic surgery). With the VATS method, the tissues between the ribs are not damaged and there is no need for sutures that approach the ribs, since it is a minimally invasive chest surgery. The patient has less pain and bleeding. Endoscopic thoracic sympathotomy (ETS) is a surgical method used to treat problems with excessive sweating in patients, mainly on the hands and armpits. In the ETS method, an opening of 1-1.5 cm wide is opened in the patient’s armpit and penetrated into the chest cavity. There is a sympathetic nerve that causes sweating when the interior is observed with a camera system (VATS). Depending on the sweating of the hands or armpits, the level of blockage is determined with the help of a camera. The operation is performed according to the technique to be performed. Robotic surgery (RATS-Robotic thoracic surgery). The logic that applies to the robotic surgery method, also called RATS, is the same as the VATS method. This method can be used in diseases where there is no excessive invasion and adhesions. The robotic method can be preferred in all diseases where thoracic surgery can be used. The advantages of robotic surgery are:
- Risk of bleeding is lower due to the surgeon’s knowledge of anatomy and ability to use wrist movements in tight spaces
- Controlled movement reduces the risk of air leaking into the lungs
- Shorter hospital stay for the patient
- Smaller incision size than open surgery
- Less risk of complications compared to open surgery
- Postoperative pain is less than with open surgery
Memorial Hospital Organ Transplant Center is the first private medical institution in Turkey to receive a license from the Health Department for organ transplantation (liver and kidney) and related laboratory services.
Liver Transplant at Memorial Ataşehir The most common indication for surgery is severe liver cirrhosis, most often caused by hepatitis B. The disease causes liver failure, which prevents the patient from leading a normal life. Congenital liver diseases and tumors can also be the cause. Memorial Ataşehir Hospital performs liver transplants from related donors (up to 4th generation) and, if approved by the Regional Ethics Committee, unrelated liver transplants. When a patient’s relative is willing to donate but does not match his or her blood type, the hospital performs a cross-transplant (exchange of donors between several donor-recipient pairs)).
Kidney transplantation In the terminal stages of kidney damage, Memorial Ataşehir performs organ transplantation from a donor relative. Another unique opportunity of the clinic’s transplant center is performing kidney transplantation operations on newborns and children under 5 years of age. The experience of Memorial Ataşehir transplantologists and the availability of special microinstruments allow such an intervention to be carried out as gently as possible.
Deficiency and excess of hormones secreted by the endocrine glands, which are organs of the endocrine system, and tumors of these glands are the subject of endocrinology. In addition, diabetes, obesity, nutrition and diet, high cholesterol and triglycerides (fats in the blood), high uric acid, metabolic syndrome, vitamin (especially vitamin D) and mineral (especially calcium) metabolism, and osteoporosis (diseases of bone metabolism such as dissolution) are included in the field of endocrinology. The endocrinology department treats patients with diseases of the endocrine organs and systems: pituitary insufficiency (HYPOPITUITARISM), excess prolactin hormone (PROLACTINOMA), excess cortisol hormone (KSHING’S DISEASE), excess growth hormone (GH) (ACROMEGAL), growth hormone deficiency and short stature (mainly a subject of pediatric endocrinology, but can sometimes be observed in adults), goiter (enlargement of the thyroid gland), thyroid overload (HYPERTHROID/toxic goiter), hypothyroid thyroid insufficiency (HYPOTHYROID), nodular diseases of the thyroid gland, inflammatory diseases of the thyroid gland (THYROIDITIS), etc.
The check-up at Memorial Ataşehir Clinic depends on many factors: gender, age, patient complaints, etc. It is important to know that:
Consultations and examinations are planned individually in accordance with the patient’s needs and health status
Preventive diagnostics are aimed at identifying oncological, cardiac and other critical diseases
Specialists assess the patient’s lifestyle, helping to determine the risk of developing diseases and take the necessary preventive measures to protect against them. They also give valuable advice on healthy eating and the necessary physical activity so that you are always in shape and feel good
Examinations are carried out within 1-2 days.
To determine the contents of the check-up and find out the prices, contact us.



Prices
Book a consultation today and get your questions answered
Reviews
On February 16, 2026, I applied to Memorial Ataşehir Hospital for a check-up. Although I confirmed my appointment via mobile application and phone, when I arrived at the hospital at 09:00, I was told that my record was not visible in the system and I was kept waiting for a while. Later, my procedures were initiated.
I was charged 33,000 TL for the check-up package. In my first consultation with the internal medicine doctor, I stated that I have an enlarged spleen and that the purpose of my check-up was specifically to investigate this condition. Following this, an additional fee of 10,500 TL was requested and collected from me.
However, during the procedures, there were serious deficiencies in terms of organization and service quality.
Specifically:
• I concluded that the doctor performed the abdominal and thyroid ultrasound procedures carelessly and superficially.
• I have had nodules in my thyroid for 25 years. I have not been receiving active treatment for the last 3-4 years, but the presence of nodules is confirmed by previous reports.
• The doctor who performed the ultrasound only made a brief assessment stating "thyroid is shrunken, no mass," completing the procedure very quickly and superficially.
• My previous test results were not reviewed.
• It was stated that the stomach and pancreas could not be visualized during the abdominal ultrasound; despite specifically mentioning my complaints of spleen enlargement and pain, it was deemed "normal," and no detailed examination was performed.
• Although a mass was detected in the uterus by the gynecologist, the ultrasound doctor stated, "I did not see it."
This situation has raised suspicions that the examinations were not performed with sufficient care and attention.
Since my test results were not available as of 4:45 PM on the same day, my other doctor appointments were postponed to another date (February 20, 2026). Therefore, my check-up service was not actually completed.
In my telephone complaint, I only requested the following:
• That the thyroid and spleen ultrasound be performed again by a different doctor when I come on February 20, 2026.
However, in the response I received, my request was rejected with the statement "the report has been reviewed, there is no error."
However, my request was not for error detection;
• That the current report contradicts my previous reports,
• That I believe the examination was performed carelessly,
• That it be re-evaluated by another specialist.
Furthermore, I requested a refund of the extra fee charged even though no further examination regarding the spleen was performed; This request of mine has also been rejected.
In conclusion:
• The check-up service was provided incompletely and carelessly.
• An extra fee was charged, but sufficient procedures were not performed in return for this fee.
• The health service was not performed properly.
• The patient's right to be informed and to receive reliable health services was violated.
For these reasons;
I request:
1. That the thyroid and spleen ultrasound be performed again by a different specialist,
2. That the additional 10,500 TL be refunded,
3. That the check-up service be completed fully and properly.
Otherwise;
I will apply to the Ministry of Health, CİMER (Presidential Communication Center) and the relevant legal authorities to exercise my legal rights. Translated fromTurkish
I would also like to thank Professor Kamil Özdil, who diagnosed my illness, which had remained undiagnosed for 3 years, by taking me step by step. He is a very competent doctor in his field. Translated fromTurkish
The staff was really helpful and theyre were people who spoke English and Arabic